Define Hydraulic (Seepage Analysis)
The options available in the Define Hydraulic Properties dialog correspond to the Groundwater Method specified in the Project Settings dialog. If the Groundwater Method = Finite Element Analysis, then you will be able to define the permeability characteristics for your materials.
Material permeability is required by the finite element analysis in order to solve the seepage problem (i.e. determine the flow and pore pressure distribution throughout the model). The available options are described below.
Saturated Permeability
A saturated permeability, Ks, must always be specified for a material. However, note:
- If you are using a User Defined Permeability Function (see below for details), then the saturated permeability is specified as the first point of the permeability function (i.e. permeability at matric suction = 0). In this case, the saturated permeability option, Ks, will be disabled.
- For all other permeability function models (i.e. Simple, van Genuchten etc), the saturated permeability Ks is enabled.
Anisotropic Permeability Parameters
Anisotropic permeability may be specified for a material (i.e. permeability varies with direction), by specifying a Factor and Angle, which defines the relative permeability in two orthogonal directions.
- K2 / K1 is the factor which specifies the relative permeability in the direction orthogonal to the K1 direction. NOTE that the K1 permeability is the "primary" permeability defined by the Saturated Permeability Ks, and the unsaturated permeability model you have defined in the dialog.
- K1 Angle is the angle which specifies the direction of the K1 permeability. The K1 Angle is specified relative to the positive X (horizontal) direction, as indicated by the picture in the dialog.
EXAMPLE: if K2 / K1 = 0.5 and K1 Angle = 0, then the permeability in the HORIZONTAL direction = Ks (in the saturated zone), and the permeability in the VERTICAL direction = 0.5 * Ks (in the saturated zone).
- K1 Surface option allows the user to assign an anisotropic surface (created in Boundary menu) to the K1 angle.
Water Content
The water content values OR degree of saturation values must be defined when the Groundwater Method = Finite Element Analysis (Steady State or Transient) in the Project Settings dialog. They are used to define the Soil Water Characteristic Curves (SWCC) when computing unsaturated soil permeabilities.
- WC sat: the saturated water content. It must be greater than WC res, and not greater than porosity.
- WC res: the residual water content, which the gradient
 becomes zero (where
becomes zero (where  is the volumetric water content).
is the volumetric water content).
Degree of Saturation
Similar to water content values, degree of saturation values can be defined alternatively. The residual degree of saturation and maximum degree of saturation need to be inputted. The relationship between water content and degree of saturation is:


 is the porosity,
is the porosity,  is the residual water content,
is the residual water content,  is the residual degree of saturation,
is the residual degree of saturation,  is the saturated water content,
is the saturated water content,  is the maximum degree of saturation.
is the maximum degree of saturation.Mv
Mv is the coefficient of water volume change. The mv parameter input is available when the Groundwater Method = Finite Element Analysis (Steady State or Transient) in the Project Settings dialog. Note that this option will not be available for coupled consolidation analysis (i.e., Consolidation Option = Coupled (Biot)).
In RS2, the mv parameter can be inputted with four options:
- None
- a constant value is calculated as the slope of water content curve at zero matric suction and is capped at 0.002.
- Constant
- user inputs a constant value.
- Fluid
- only fluid is considered.
- 1D Elastic consolidation
- 1D elastic uncoupled consolidation is considered.
- 2D Elastic consolidation
- 2D plane-strain elastic uncoupled consolidation is considered.
- In a transient groundwater analysis, the mv parameter calculations for unsaturated soils is different from that for fully saturated soils.
- It is known that the saturated and unsaturated flows are considered differently in groundwater analysis. When a transient analysis is enabled, the saturated groundwater flow is controlled by the mv parameter (besides soil permeability), while the water content does not change; the unsaturated groundwater flow is governed by both the mv parameter and the water content curve.
- The mv parameter will have no impact on a steady state groundwater analysis.
- Theories and equations about mv parameter can be found in the Groundwater Seepage document.
Permeability Models
The following models are available in RS2 for describing the permeability in the unsaturated zone as a function of matric suction.
- Simple
- Fredlund and Xing
- van Genuchten
- Brooks and Corey
- Gardner
- Constant
- User Defined
Plot Function 
This option is available for all permeability models except for the User Defined model. The permeability function and water content function (SWCC) will be plotted based on the defined model and inputted parameters. Use this option after model and parameters have been selected and entered.
For User Defined models, the permeability function and water content function (SWCC) are plotted by user defined data. A set of permeability vs. matric suction, and a set of water content vs. matric suction data need to be inputted. See the User Defined section for more details.
Pick button ![]()
This option is available for Simple, Fredlund and Xing, van Genuchten, Brooks and Corey, and Gardner models. If you select the Pick button you will see another dialog, from which you can select from a list of materials, with representative parameters for the selected model. (References for the data are provided in the dialog). If you select [OK] in this dialog, the currently selected parameters will be automatically loaded into the Define Hydraulic Properties dialog.
SIMPLE
With the Simple model, an unsaturated permeability function is automatically determined by RS2 based on the magnitude of the saturated permeability Ks and the selected Soil Type. To view the function determined by RS2, you can select the Plot button in the dialog. For the Simple model, you can choose one of the following Soil Types:
- General
- Sand
- Silt
- Clay
- Loam
For the General soil type, the unsaturated permeability simply decreases by an order of magnitude within the initial range of matric suction values, and then remains constant for higher values of suction.
For specific soil types (Sand, Silt, Clay or Loam) average curves have been determined from typical literature values.
FREDLUND AND XING
The following equation defines the Fredlund-Xing permeability function (Fredlund and Xing, 1994):
![]() Eqn.2
Eqn.2
where: A, B and C are the model parameters
![]() = 2.7182818 …
= 2.7182818 …
![]() = matric suction
= matric suction
K = permeability
Ks = saturated permeability
VAN GENUCHTEN
The following equations define the van Genuchten permeability function (van Genuchten, 1980):
![]() Eqn.4a
Eqn.4a
![]() Eqn.4b
Eqn.4b
where: ![]() = degree of saturation
= degree of saturation
h = pressure head (suction)
![]() are the model parameters
are the model parameters
K = permeability
Ks = saturated permeability
NOTE: the parameters m and n are related as follows:
![]() Eqn. 4c
Eqn. 4c
However, you can specify a value of m which is independent from n, by selecting the Custom m check box, and entering a value for m.
BROOKS AND COREY
The following equations define the Brooks-Corey permeability function (Brooks and Corey, 1964):
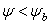 :
: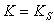 Eqn.1a
Eqn.1a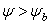 :
: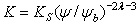 Eqn.1b
Eqn.1b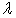 = Pore size index
= Pore size index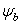 = bubbling pressure
= bubbling pressure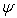 = matric suction
= matric suctionK = permeability
Ks = saturated permeability
GARDNER
The following equation defines the Gardner permeability function (Gardner, 1956):
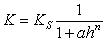 Eqn.3
Eqn.3where: a and n are the model parameters
h = pressure head (suction)
K = permeability
Ks = saturated permeability
USER DEFINED
For complete flexibility in defining permeability functions, User Defined Permeability and Water Content functions can be defined, as follows:
- Select the Define button in the Define Hydraulic Properties dialog.
- You will see the User Defined Permeability and Water Content dialog.
- Enter a Name for the function.
- Select the Permeability tab and enter the Matric Suction and Permeability values, which define the required function. As you enter the data, the graph at the right of the dialog, will display the function you are defining.
- The water content can be defined either By Water Content data or By Degree of Saturation data, as selected from the WC Input Type dropdown menu at the top. Select the Water Content tab if By Water Content type is used or select the Degree of Saturation tab if By Degree of Saturation type is used. Enter the Matric Suction and Water Content/Degree of Saturation values in the grid, which define the required function. As you enter the data, the graph at the right of the dialog, will display the function you are defining.
- When all data has been entered, select [OK], and you will be returned to the Define Hydraulic Properties dialog.
- In the Define Hydraulic Properties dialog, the Name of the User Defined Permeability and Water Content you have defined, will now appear in the Model drop-list. It can now be selected at any time, just like any of the other permeability models.
NOTE: the data points on the graph can be moved graphically by clicking on them with the mouse and dragging.
The following options allow you to edit, delete, copy, import or export User Defined Permeability Functions.
Edit
To modify an existing User Defined Permeability Function, select the Name of the function from the Model list, and select the Edit button. You can then edit the data which defines the function, in the User Defined Permeability Function dialog.
Delete
To delete an existing User Defined Permeability Function, select the Name of the function from the Model list, and select the Delete button.
Copy
To create a copy of an existing User Defined Permeability Function, select the Name of the function from the Model list, and select the Copy button. Enter a new name in the dialog which appears, and select [OK]. A new function will automatically be created, and the Name will appear in the Model list.
Import / Export
User Defined Permeability Functions in RS2 can be saved in their own separate file, if desired.
- To save a User Defined Permeability Function file, select the Export button in the User Defined Permeability Function dialog. These files have a .FN5 filename extension.
- To import a User Defined Permeability Function file, select the Import button in the User Defined Permeability Function dialog.