Gamma Distribution
The Gamma distribution is widely used in engineering, science, and business, to model continuous variables that are always positive and have skewed distributions. In Slide, the Gamma distribution can be useful for any variable which is always positive, such as Cohesion for example.
The Gamma distribution has the following probability density function:
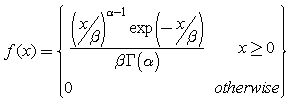
where Γ(α) is the Gamma function, and the parameters α and β are both positive, i.e. α > 0 and β > 0.
- α is known as the shape parameter, while β is referred to as the scale parameter.
- β has the effect of stretching or compressing the range of the Gamma distribution. A Gamma distribution with β = 1 is known as the standard Gamma distribution.
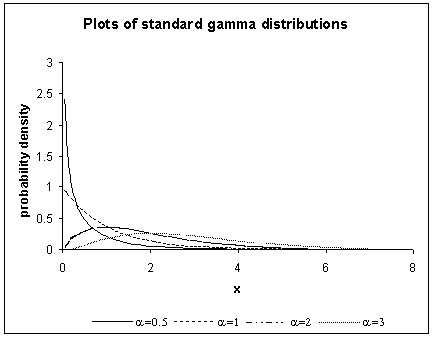
The Gamma distribution represents a family of shapes. As suggested by its name, α controls the shape of the family of distributions. The fundamental shapes are characterized by the following values of α:
Case I (α < 1)
When α < 1, the Gamma distribution is exponentially shaped and asymptotic to both the vertical and horizontal axes.
Case II (α = 1)
A Gamma distribution with shape parameter α = 1 and scale parameter β is the same as an exponential distribution of scale parameter (or mean) β.
Case III (α > 1)
When α is greater than one, the Gamma distribution assumes a mounded (unimodal), but skewed shape. The skewness reduces as the value of α increases.
Examples of shapes of the standard Gamma distributions with different values of α are shown in the figure below.
The shape and scale parameters of a Gamma distribution can be calculated from its mean m and standard deviation s according to the relationships:
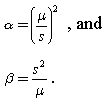
From the expression for a, it can be seen that:
- Case I of the Gamma distribution’s shape occurs when the mean m is less than the standard deviation s.
- Case II – the case of the exponential distribution – occurs when the mean is equal to the standard deviation.
- The third shape of the Gamma distribution arises when the mean is greater than the standard deviation.
The Gamma distribution is sometimes called the Erlang distribution when its shape parameter α is an integer.