Bolt Force Diagrams
A Bolt Force Diagram, as defined in RocPlane, represents the available Tensile Force that a bolt can apply to a wedge at any point along the length of the bolt. That is, if a wedge plane intersects a bolt at a certain location along its length, what is the maximum Tensile Support Force that the bolt can apply to the wedge. This assumes that the bolt is mobilized in pure tension.
- For Mechanically Anchored bolts, the Bolt Force Diagram is simply a horizontal line, since a constant support force is applied, regardless of where a wedge plane intersects the bolt.
- For Grouted Dowel, Cable, or Split Set or Swellex bolts, the Bolt Force Diagram is determined by considering each possible tensile failure mode along the length of the support (Tensile, Pullout and Stripping, if applicable). The Bolt Failure Mode that generates the MINIMUM force determines the support force that can be generated, at each point along the support.
- For User Defined Support, the Bolt Force Diagram is defined explicitly by the user and tensile properties (e.g., Tensile Strength, Plate Capacity, Bond Strength) are not entered.
For example, a possible Bolt Force Diagram for a Grouted dowel with a Bond Length of less than 100%, and a Plate Capacity that is less than the Tensile Capacity is illustrated below.
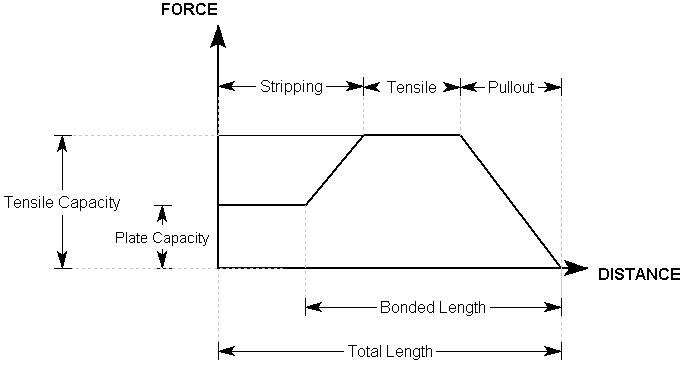
Bolt Force Diagram for Grouted dowel
For more examples of typical Bolt Force Diagrams, see the following topics:
In addition to the Bolt Force Diagram, there are two other factors that ultimately determine the support force that can be supplied by a bolt in RocPlane: Bolt Orientation Efficiency and Bolt Shear Strength.
For an overview of the bolt support implementation in RocPlane, see Bolt Support Force in RocPlane topic. This discusses all of the parameters that affect the bolt support capacity and summarizes all possible cases.
Interpretation of Bolt Force Diagrams
The user should appreciate that a Bolt Force Diagram, as implemented in RocPlane, does not necessarily represent the true state of stress or loading mobilized by a given bolt. The diagram simply represents the maximum available Tensile Force a given bolt can theoretically apply to a wedge at any point along its length. This is based on the assumptions described for each bolt type in RocPlane.
Remember that the RocPlane analysis is a limit equilibrium analysis. Displacements and strains are not considered in such an analysis. In order to realistically model the interaction of support and excavation, and to calculate actual strains and loading mobilized within the support, more sophisticated numerical analysis methods are required, such as finite element or finite difference methods.
The modeling of support in RocPlane is a simple but useful method of accounting for the effect of the support system on the wedge in a limit equilibrium analysis. It is not intended to model the effect of the wedge on the support system, and the Bolt Force Diagrams should not be interpreted in this way.